Sharks.
South East Queensland Marine Aquarium and Ocean activities Forum :: SEQMAOAF :: Local marine life found in SEQ and information.
Page 1 of 1
 Sharks.
Sharks.
Juv wobby

Adult wobby

Fight to death between wobby and ocy

White tip

Whale shark

Bull shark

Sand whaler shark

Leopard shark

Grey nurse

Chiloscyllium punctatum or cat shark and as an adult, a dog shark!
Upon hatching these are referred to as cat sharks before turning grey.
The dog shark eats inverts mainly, which includes oysters and muscles that they crush with their powerful crushers plates, due to not having actual teeth.
The juveniles can be hard to start them feeding, so it is best to collect small inverts like glass or peppermint shrimp and small squid to start them off, then they will feed on squid, prawns, what ever in relation to inverts.
These are found in eggs attached to algae on the protected shallow side of islands, reefs in bays and estuaries from November and can take up to four months for incubation.
At times the eggs will become dislodged and be moved by currents and choppy waters.
If you find an egg, look at it carefully to see the colour bands through the casing and if the time of year is past or at early to late January, then cut it open and sit the shark with its egg sack in a perforated container and wait till its sack is gone or rejected and its ready for aquarium life.
Shark container.
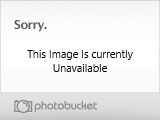
Shark in that container protected while it grows and feeds off its egg sack.
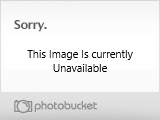
You can place the egg in the current as it has an opening each end to allow oxygenated waters to pass through so that the growing shark inside has oxygen.
Juvenile colours.

Sub adult
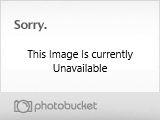
Adult dog shark

Information on raising a cat shark.
https://southeastqueenslandm.aforumfree.com/t2139-raising-your-own-cat-shark

Adult wobby

Fight to death between wobby and ocy

White tip

Whale shark

Bull shark

Sand whaler shark

Leopard shark

Grey nurse

Chiloscyllium punctatum or cat shark and as an adult, a dog shark!
Upon hatching these are referred to as cat sharks before turning grey.
The dog shark eats inverts mainly, which includes oysters and muscles that they crush with their powerful crushers plates, due to not having actual teeth.
The juveniles can be hard to start them feeding, so it is best to collect small inverts like glass or peppermint shrimp and small squid to start them off, then they will feed on squid, prawns, what ever in relation to inverts.
These are found in eggs attached to algae on the protected shallow side of islands, reefs in bays and estuaries from November and can take up to four months for incubation.
At times the eggs will become dislodged and be moved by currents and choppy waters.
If you find an egg, look at it carefully to see the colour bands through the casing and if the time of year is past or at early to late January, then cut it open and sit the shark with its egg sack in a perforated container and wait till its sack is gone or rejected and its ready for aquarium life.
Shark container.

Shark in that container protected while it grows and feeds off its egg sack.

You can place the egg in the current as it has an opening each end to allow oxygenated waters to pass through so that the growing shark inside has oxygen.
Juvenile colours.

Sub adult

Adult dog shark

Information on raising a cat shark.
https://southeastqueenslandm.aforumfree.com/t2139-raising-your-own-cat-shark
_________________
Forum Admin

liquidg- Posts : 2782
Join date : 2010-02-02
Location : Brisbane bayside
 Similar topics
Similar topics» Sharks off straddie
» Two headed sharks?
» Sharks on east Aus coast.
» Grey nurse sharks in abundance.
» Dave and Ross at Ningaloo with the whale sharks.
» Two headed sharks?
» Sharks on east Aus coast.
» Grey nurse sharks in abundance.
» Dave and Ross at Ningaloo with the whale sharks.
South East Queensland Marine Aquarium and Ocean activities Forum :: SEQMAOAF :: Local marine life found in SEQ and information.
Page 1 of 1
Permissions in this forum:
You cannot reply to topics in this forum
 Home
Home